What is Format Specifier
The format specifier is a way to tell your compiler what type of data are you dealing with. It is used while inputting and outputting any data. For all format specifiers, you can check this chart or complete article here
General Syntax in printf()
printf("%a.b{formatSpecifier}", yourvariable);
where a and b are integers where a tells total character spaces for output and b tells the accuracy after the decimal.
Let's look at this code for more details
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float b = 5.63;
printf("%6.3f\n", b);
return 0;
}
// output
5.630
In the above code, there a=6 and b=3 means we will have 3 decimal places and if we look closely there is 1 space before 5 in the output 4 character spaces by 5, 6, 3 and 0 and fifth by . but we said 6 so it added a space before because a was positive if a would have been negative it will add spaces after the output.
General Syntax in scanf()
scanf("%{formatSpecifier}", &yourvariable);
Sample Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
float a;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%f", &a);
printf("Your Input Is: %7.3f", a);
return 0;
}
// output
Enter a number: 5.32
Your Input Is: 5.320
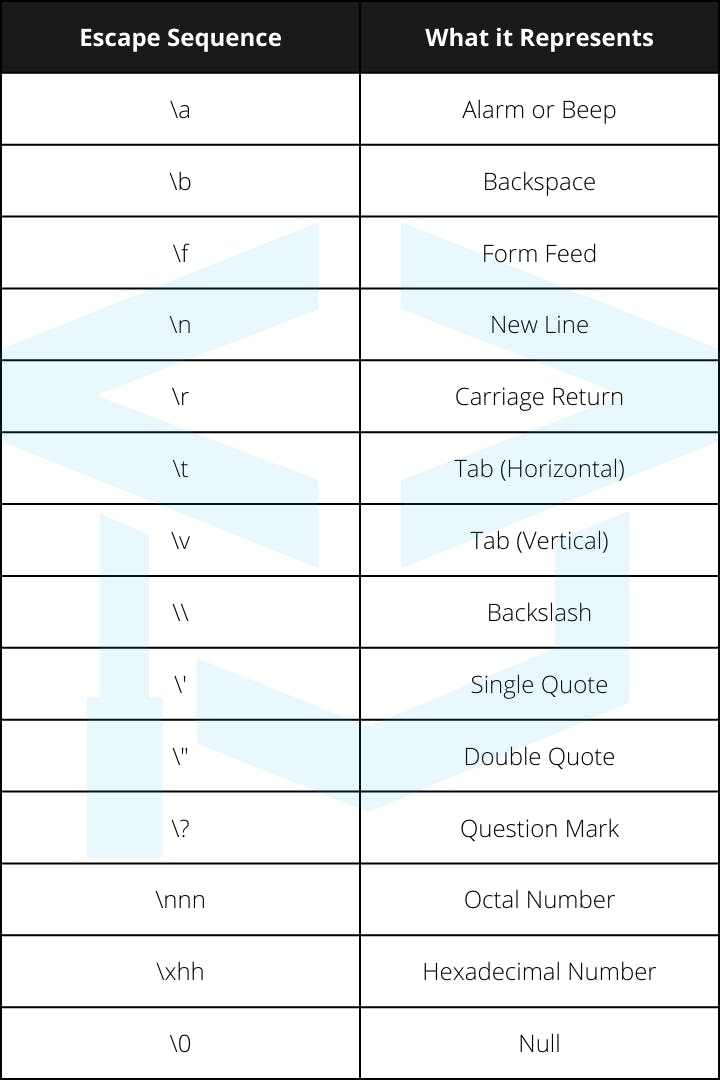
What is Escape Sequence
In C, an escape sequence is a character sequence that cannot be used directly in a string literal. You need more character starting with backslash . For example, \n represents new line.
List of Escape Sequence in C
Sample Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int number=50;
printf("We\nareC\b learning\t\"C\" programming here \'on\' CodeWithRish");
return 0;
}
// output
We
are learning "C" programming here 'on' CodeWithRish

